Genetic Variation and Change
This topic is about how traits are inherited. (Mendelian Genetics) The topic leads on to how the alleles are expressed in the phenotype. The outcome of the phenotype is dependent upon the environment. In the long term this leads to changes in the gene pool and evolutionary change.
The first step in understanding this topic is ensuring that some of the ideas about cell division and especially meiosis are clear in you mind.
The first step in understanding this topic is ensuring that some of the ideas about cell division and especially meiosis are clear in you mind.
|
Beside is a link to a slide show which explains why Meiosis is so important.
Below is a reminder of the process of meiosis |
Meiosis from Sawyer Science |
|
This next clip is about 20 mins and goes through our understanding of inheritance as it developed over time. It introduces us to Menedelian genetics and explains the basics leading into this topic.
|
|
|
This is a doco which outlines the life of Mendel and explains his life and history which lead to his famous set of experiments.
|
|
Mendelian Genetics
The next link is to Cold Spring Harbour, internationally famous for genetic research. This is a series of tutorials on basic genetics where you can get the basics and explore concepts in more depth.
Below are 2 clips from Youtube. Basic introduction to chromosomes, genes and alleles: Revision of Year 11. Both clips are quite short and will refresh those memory cells of yours!!
|
|
|
This next site is dedicated to explaining basic genetics and is worth exploring. It is developed by Utah university and is recognized as being a very sound learning platform for you to use.
Understanding Pedigree Diagrams
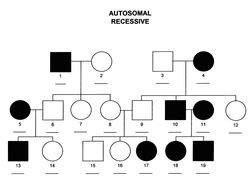
The diagram below is a typical pedigree diagram. you should be able to interpret these easily. This one has 3 generations represented.
Individuals 1,2,3 & 4 are the parental generation, called the P1. Individuals 5-12 are the next generation and are called the F1. (These are the first children born from the P1 generation)
The individuals 13- 19 are the next generation and are called the F2. They are the grandchildren of the P1 and the children of the F1.
Lines show how marries who and the lines show where those individuals came from (if known). The order of birth of the children is from left to right, so individual 6 is the first child, born before individual 7. Males are the squares and females the circles. Individuals who have the condition are usually shaded.
Just a wee explanation: "P " represents the original Parents. The "F" comes from the word "filial" meaning brothers (and sisters), so these are the children who are the brothers and sisters.
Individuals 1,2,3 & 4 are the parental generation, called the P1. Individuals 5-12 are the next generation and are called the F1. (These are the first children born from the P1 generation)
The individuals 13- 19 are the next generation and are called the F2. They are the grandchildren of the P1 and the children of the F1.
Lines show how marries who and the lines show where those individuals came from (if known). The order of birth of the children is from left to right, so individual 6 is the first child, born before individual 7. Males are the squares and females the circles. Individuals who have the condition are usually shaded.
Just a wee explanation: "P " represents the original Parents. The "F" comes from the word "filial" meaning brothers (and sisters), so these are the children who are the brothers and sisters.
Di Hybrid Crosses: 2 characteristics at once
|
Beside is a link on How to do dihybrid crosses: a 10 minute excellent presentation on how to solve these using punnett squares.
A good quick tutorial on how to do dihybrid crosses. Also a good link to haploid and diploid cells.
|
|
This is a chapter with some good animations etc on Crossing over and linkage. It goes into details of meiosis. A reminder you do not need to know the stages in detail but you need an overview.
Below is a gateway to a big library of good online learning information relating to genetics.
Evolution and Change
Natural Selection: the "survival of the fittest"
Natural selection is one of the main processes that acts to "fuel" the change in species over time. It relies on the fact that more individuals of a species/population are born than can survive if resources such as food are limited. So the "weaker individuals do not survive to reproduce. (They end up dead before they have babies and don't pass on their genes to the next generation.)
This process relies on the fact that there is variation in the individuals, some are better adapted than others in a population to survive. This is because they have inherited "better" alleles from their parents. (Use the word "advantageous", not "better" to make your explanation more scientific)
This process relies on the fact that there is variation in the individuals, some are better adapted than others in a population to survive. This is because they have inherited "better" alleles from their parents. (Use the word "advantageous", not "better" to make your explanation more scientific)
A funny little animation and game to play on natural selection:
|
Natural selection in action: Pocket mouse in a volcanic environment. Research
|
|
Three main types of natural selection are recognized:
1. Stabilizing
2. Disruptive
3. Directional
In addition some populations show no selection. this happens when there is no shortage of resources and the population is in balance with the resources in the environment.
Sexual selection also occurs. This is when organisms choose their sexual partners due to favourable characteristics. Mating is not random. This means that the individuals that do mate pass on more of their alleles to the next generation.
1. Stabilizing
2. Disruptive
3. Directional
In addition some populations show no selection. this happens when there is no shortage of resources and the population is in balance with the resources in the environment.
Sexual selection also occurs. This is when organisms choose their sexual partners due to favourable characteristics. Mating is not random. This means that the individuals that do mate pass on more of their alleles to the next generation.
Gene pools and evolution
|
This clip is a 3 min explanation of founder effect, bottleneck and genetic drift situations.
|
|
|
The next link is to a good animation on genetic drift and how it works. It includes an online quiz to test your understanding of the concepts introduced.
|
|
What is a species? This next link is to an explanation from Berkley University. Their explanation is quite clear and there are other sections you could explore to extend yourself and test your understanding.
|
|
The next power point is an overall summary to explain this whole section on evolution.
|
